What's Inside Cilium's KVStore (and What's Not)
In a large Cilium-powered Kubernetes cluster, there is a central repository (kvstore) that all Cilium agents will connect to. While Cilium supports several types of kvstores, the most oftenly used is etcd.
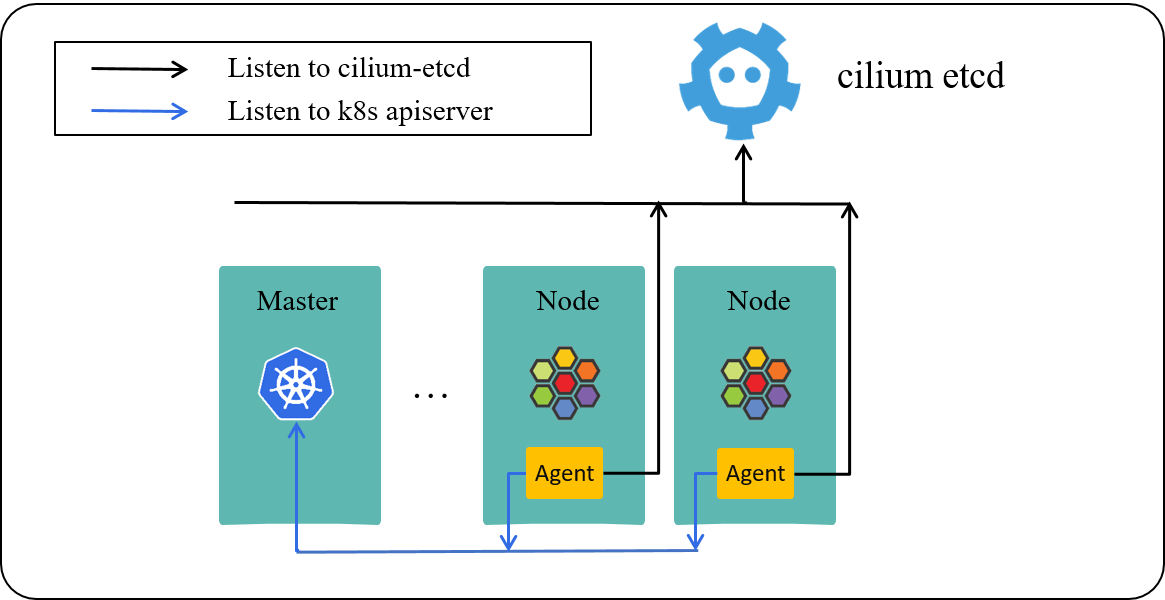
Fig. Cilium Components [1]
Then you may wonder: what exactly stuffs are stored in this kvstore? We will dig inside in this post.
1 Preparation
1.1 Environment
Software version:
- Kubernetes:
1.17+ - Cilium:
1.8.2 - Etcd (cilium kvstore):
3.2.24
other configurations:
- Cilium networking solution: direct routing via BGP [2]
Note that some command line outputs in this post are re-formatted for better human viewing.
Do not rely on the output formats in this post if you are automating something.
We will execute commands on the following types of nodes:
- k8s worker nodes
- k8s master nodes
- cilium-etcd nodes
1.2 Cilium-etcd information
On k8s worker node:
(k8s node) $ cilium status
KVStore: Ok etcd: 3/3 connected, ... https://10.5.2.10:2379; https://10.5.2.11:2379; https://10.5.2.12:2379 (Leader)
Kubernetes: Ok 1.17+ [linux/amd64]
...
As shown in the output, we are connected to 3 etcd instances.
I can run cilium command on worker nodes because cilium is a wrapper
here:
(k8s node) $ cat /usr/local/bin/cilium
#!/bin/bash
CID=`sudo docker ps | awk '/cilium-agent/ {print $1}'`
sudo docker exec $CID cilium $@
1.3 Setup etcdctl
On etcd node:
(etcd node) $ cat /etc/etcd/etcdrc
export ETCDCTL_API=3
export ETCDCTL_ENDPOINTS="https://127.0.0.1:2379"
export ETCDCTL_CACERT=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.crt
export ETCDCTL_CERT=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-client.crt
export ETCDCTL_KEY=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-client.key
Test:
(etcd node) $ source /etc/etcd/etcdrc
(etcd node) $ etcdctl endpoint health
127.0.0.1:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 2.67051ms
(etcd node) $ etcdctl member list
e7c82b4ad3edb47, started, etcd-node1, https://10.5.2.10:2380, https://10.5.2.10:2379
d0c026e8a84e61d4, started, etcd-node2, https://10.5.2.12:2380, https://10.5.2.12:2379
f13a3cd92f97eadd, started, etcd-node3, https://10.5.2.11:2380, https://10.5.2.11:2379
2 What’s inside cilium-etcd
First, have a glimpse of all keys in etcd:
$ etcdctl get "" --prefix --keys-only
cilium/state/identities/v1/id/10004
...
cilium/state/nodes/v1/default/node1
...
cilium/state/ip/v1/default/10.6.36.43
...
Strip blank lines and redirect to file:
$ etcdctl get "" --prefix --keys-only | grep -v "^$" > keys.txt
In my environment, those dumped keys group into 3 types:
- pod identities
- pod ip addresses
- k8s nodes
2.1 Identity
Dump the content (value) of a specific identity:
$ etcdctl get cilium/state/identities/v1/id/12928
k8s:app=istio-ingressgateway;
k8s:chart=gateways;
k8s:heritage=Tiller;
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=default;
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=ai-ingressgateway-service-account;
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=istio-system;
k8s:istio=ai-ingressgateway;
k8s:release=istio;
These seem to be Pod labels, verify it on K8S master:
(k8s master) $ k get pod -n istio-system --show-labels | grep istio-ingressgateway
NAME READY LABELS
ai-ingressgateway-6bdbdbf7dc-jz85c 1/1 app=istio-ingressgateway,chart=gateways,heritage=Tiller,istio=ai-ingressgateway,pod-template-hash=6bdbdbf7dc,release=istio
Describe pod to get more detailed information:
(k8s master) $ k describe pod -n istio-system ai-ingressgateway-6bdbdbf7dc-jz85c
Name: ai-ingressgateway-6bdbdbf7dc-jz85c
...
Labels: app=istio-ingressgateway
chart=gateways
heritage=Tiller
istio=ai-ingressgateway
pod-template-hash=6bdbdbf7dc
release=istio
Annotations: sidecar.istio.io/inject: false
IP: 10.6.6.43
...
That’s it!
As we can see, Cilium picks up some (not all, e.g. pod-template ignored)
labels from K8S, and appends them with k8s:, then stores to cilium-etcd:
app=istio-ingressgatewaychart=gatewaysheritage=Tilleristio=ai-ingressgatewayrelease=istio
Besides, it also adds its own labels:
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=defaultk8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=ai-ingressgateway-service-accountk8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=istio-system
Note that pod label pod-template-hash=6bdbdbf7dc is not stored into etcd
(ignored by Cilium).
2.2 Labels -> Identity
2.3 Pod IP Address
In the k describe pod output, we get some additional information:
- Pod IP:
10.6.6.43 - Node:
k8s-node1 - PodCIDR:
10.6.6.0/24
Now dump the IP address information in cilium-etcd:
$ etcdctl get cilium/state/ip/v1/default/10.6.6.43
{
"IP":"10.6.6.43",
"Mask":null,
"HostIP":"10.5.1.132",
"ID":12928,
"Key":0,
"Metadata":"cilium-global:default:k8s-node1:432",
"K8sNamespace":"istio-system",
"K8sPodName":"ai-ingressgateway-6bdbdbf7dc-jz85c"
}
2.4 Kubernetes Node
Dump the node information:
$ etcdctl get cilium/state/nodes/v1/default/k8s-node1
{
"Name":"k8s-node1",
"Cluster":"default",
"IPAddresses":[{"Type":"InternalIP", "IP":"10.5.1.132"},
{"Type":"CiliumInternalIP", "IP":"10.6.6.71"}],
"IPv4AllocCIDR":{"IP":"10.6.6.0", "Mask":"////AA=="},
"IPv6AllocCIDR":null,
"IPv4HealthIP":"10.6.6.79",
"IPv6HealthIP":"",
"ClusterID":0,
"Source":"local",
"EncryptionKey":0
},
Where:
InternalIP: node IP addressIPv4AllocCIDR: PodCIDR for this node, used by Cilium agentCiliumInternalIP: Cilium’s gateway IP (configured oncilium_host) on this node, allocated from PodCIDRIPv4HealthIP: Cilium’s health check IP address on this node, allocated from PodCIDR
2.4.1 IPv4AllocCIDR
(k8s master) $ kubectl describe node k8s-node1 | grep PodCIDR
PodCIDR: 10.6.6.0/24
PodCIDRs: 10.6.6.0/24
2.4.2 CiliumInternalIP
(k8s-node1) $ ifconfig cilium_host
cilium_host: flags=4291<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,NOARP,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.6.6.71 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 0.0.0.0
...
2.4.3 IPv4HealthIP
(k8s-node1) $ cilium endpoint list | awk 'NR == 1 || /reserved:health/'
ENDPOINT POLICY (ingress) POLICY (egress) IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv4 STATUS
3030 Disabled Disabled 4 reserved:health 10.6.6.79 ready
3 What’s NOT inside cilium-etcd
Re-depict the above picture for better illustration:

3.1 Cilium network policy (CNP)
Cilium network policy (CNP) stores in k8s apiserver.
(k8s master) $ kubelet get cnp
NAME AGE
cnp-test 10d
Cilium agents listen to apiserver, and cache them locally:
(node) $ cilium policy get
[
{
"endpointSelector": {
"matchLabels": {
"any:cnp": "test",
"k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace": "default"
}
},
"ingress": [
{
"fromEndpoints": [
{
"matchLabels": {
"any:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace": "default",
"any:cnp": "apitest"
}
}
],
...
(node) $ cilium bpf policy get --all
/sys/fs/bpf/tc/globals/cilium_policy_02489:
DIRECTION LABELS (source:key[=value]) PORT/PROTO PROXY PORT BYTES PACKETS
Ingress reserved:unknown ANY NONE 10359922482 1736082
Ingress reserved:host ANY NONE 0 0
Ingress reserved:remote-node ANY NONE 0 0
Egress reserved:unknown ANY NONE 2106265974 13269635
...
On agent restart or node reboot, Cilium agents will recreate them from apiserver.
3.2 Endpoint
Cilium’s Endpoint is a node-local concept, that is, EndpointID is meaningless
out of the node that created it, and EndpointIDs are overlapping among different
nodes.
(node1) $ cilium endpoint list
ENDPOINT IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv4 STATUS
2489 42222 k8s:app=redis 10.2.2.2 ready
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
(node2) $ cilium endpoint list
ENDPOINT IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv4 STATUS
2489 43333 k8s:app=mongo 10.2.3.3 ready
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
3.3 CiliumEndpoint (CEP)
For each Endpoint, cilium-agent will create a corresponding CiliumEndpoint custom resource in Kubernetes:
(master) $ k describe cep web1-0
Name: web1-0
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: cilium.io/v2
Kind: CiliumEndpoint
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2020-09-16T10:25:56Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 2164268066
Self Link: /apis/cilium.io/v2/namespaces/default/ciliumendpoints/web1-0
UID: 9881196e-359a-4bd2-bcb8-a357e17a9441
Status:
Encryption:
External - Identifiers:
Container - Id: 34722eeca1019e273c158f2ef94bfd80c36d45f8afd48d8f547c12989ae69348
k8s-namespace: default
k8s-pod-name: web1-0
Pod - Name: default/web1-0
Id: 3139
Identity:
Id: 8419
Labels:
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
k8s:statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name=web1-0
Named - Ports:
Name: web
Port: 80
Protocol: TCP
Networking:
Addressing:
ipv4: 10.6.2.2
Node: 10.5.6.60
State: ready
Events: <none>
For each endpoint, there will be a dedicated controller to synchronize local Endpoint states to Kubernetes CEP. For more details, see Cilium Code Walk Through: CNI Create Network.
4. Summary
What’s inside cilium-etcd (key -> value):
IdentityID->IdentityLabels(PodLabels)IdentityLabels+/+NodeIP->IdentityIDPodIP->PodIPDetails(e.g. identity, host, etc)NodeName->NodeDetailsClusterMeshNodeName->ClusterMeshNodeDetails
What’s NOT inside cilium-etcd:
- CiliumNetworkPolicy (CNP): stores in k8s
- Endpoint (node local): stores in node-local files
- CiliumEndpoint (CEP): stores in k8s