OVS Deep Dive 2: OVSDB
In this OVS Deep Dive series, I will walk through the Open vSwtich source code to look into the core designs and implementations of OVS. The code is based on ovs 2.6.1.
1. OVSDB Overview
ovsdb-server provides RPC interfaces to one or more Open
vSwitch databases (OVSDBs). It supports JSON-RPC client connections over
active or passive TCP/IP or Unix domain sockets.
Each OVSDB file may be specified on the command line as database. If
none is specified, the default is /etc/openvswitch/conf.db.
OVSDB holds switch-level configurations:
- bridges, interfaces, tunnel info
- OVSDB and OpenFlow controller addresses
Configurations is stored on disk and survives reboot.
Custome database with nice properties:
- value constraints
- weak references
- garbage collection
Speaks OVSDB protocol to manager and ovs-vswitchd. CLI tools:
ovs-vsctl: modifies DB by configuringovs-vswitchdovsdb-tool: DB management, e.g. create/compact/convert DB, show DB logs
2. Key Data Structures
In this section we will have a glance at some key data structures in ovsdb.
ovsdb_schemaovsdbovsdb_serverovsdb_table_schemaovsdb_table
2.1 OVSDB
/* Database schema. */
struct ovsdb_schema {
char *name;
char *version;
char *cksum;
struct shash tables; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_table_schema *"s. */
};
/* Database. */
struct ovsdb {
struct ovsdb_schema *schema;
struct ovs_list replicas; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_replica"s. */
struct shash tables; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_table *"s. */
/* Triggers. */
struct ovs_list triggers; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_trigger"s. */
bool run_triggers;
};
2.2 OVSDB Table
/* Schema for a database table. */
struct ovsdb_table_schema {
char *name;
bool mutable;
bool is_root; /* Part of garbage collection root set? */
unsigned int max_rows; /* Maximum number of rows. */
struct shash columns; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_column *"s. */
struct ovsdb_column_set *indexes;
size_t n_indexes;
};
/* Database table. */
struct ovsdb_table {
struct ovsdb_table_schema *schema;
struct ovsdb_txn_table *txn_table; /* Only if table is in a transaction. */
struct hmap rows; /* Contains "struct ovsdb_row"s. */
/* An array of schema->n_indexes hmaps, each of which contains "struct
* ovsdb_row"s. Each of the hmap_nodes in indexes[i] are at index 'i' at
* the end of struct ovsdb_row, following the 'fields' member. */
struct hmap *indexes;
};
Open_vSwitch is the root table and there is always only a single row.
Fig.2.1 lists the most commonly used ones; a full entity-relationship diagram
is available in the ovs-vswitchd.conf.db man page.

Fig.2.1. ovsdb core tables
To list the contents of table Port:
$ ovs-vsctl list Port
_uuid : 47c10988-3fe7-4100-9cd6-733068658d2f
bond_fake_iface : false
fake_bridge : false
interfaces : [1ac53111-f844-4d78-be6c-82edfb4c485e]
lacp : []
mac : []
name : "br0"
other_config : {}
rstp_statistics : {}
rstp_status : {}
statistics : {}
status : {}
tag : []
vlan_mode : []
...
3. Flow Diagram
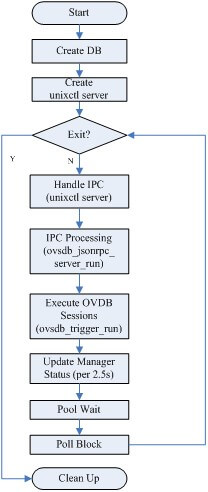
Fig.3.1. ovsdb flow diagram
ovsdb/ovsdb-server.c:
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* step.1. handle configs, open db */
SSET_FOR_EACH (db_filename, &db_filenames)
open_db(&server_config, db_filename);
/* step.2. create unixctl server and register commands */
unixctl_server_create(unixctl_path, &unixctl);
unixctl_command_register("exit", "", 0, 0, ovsdb_server_exit, &exiting);
...
/* step.3. enter main loop */
main_loop();
|--while (!*exiting) {
/* step.3.1 handle control messages from CLI and RPC */
unixctl_server_run(unixctl); // handle CLI commands (turn into RPC requests)
ovsdb_jsonrpc_server_run(jsonrpc); // handle RPC requests
/* step.3.2 ovsdb session execute */
SHASH_FOR_EACH(node, all_dbs) {
ovsdb_trigger_run(db->db, time_msec()); // execute session, commit changes
}
/* step.3.3 update Manager status(es) every 2.5 seconds */
if (time_msec() >= status_timer)
update_remote_status(jsonrpc, remotes, all_dbs);
/* step.3.4 wait events arriving */
/* step.3.5 block until events arrive */
poll_block();
}
/* step.4. clean and exit */
}
4. Procedures and Submodules
4.1 Create OVSDB
For each configured ovsdb file, ovsdb-server creates a struct ovsdb
instance. This is done in open_db().
Then, it reconfigures ovsdb-server’s
remotes by calling reconfigure_remotes(). A remote is an active or passive
stream connection method, e.g. “pssl:” or “tcp:1.2.3.4”.
In the end, it calls to the following method to re-allocate and add new remotes:
static struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_remote *
ovsdb_jsonrpc_server_add_remote(struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_server *svr,
const char *name,
const struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_options *options)
{
jsonrpc_pstream_open(name, &listener, options->dscp);
remote = xmalloc(sizeof *remote);
remote->server = svr;
remote->listener = listener;
ovs_list_init(&remote->sessions);
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_create(remote, jsonrpc_session_open(name, true),
svr->read_only || remote->read_only);
return remote;
}
Register IPC Methods
After OVSDB is created, ovsdb-server will register its CLI subcommands to
unixctl server. These subcommands could be executed with ovsdb-server.
4.2 Handle IPC Messages
In the while loop of ovs-vswitchd, unixctl_server_run() and
ovsdb_jsonrpc_server_run() are called.
unixctl server receives messages from unix IPC socket, which is
located at /var/run/openvswitch/ by default, with the name
ovsdb-server.<pid>.ctl. It then converts the message into a RCP request,
which will be handled by the jsonrpc server later.
void
unixctl_server_run(struct unixctl_server *server)
{
pstream_accept(server->listener, &stream);
conn->rpc = jsonrpc_open(stream);
LIST_FOR_EACH_SAFE (conn, next, node, &server->conns) {
run_connection(conn);
|
|--jsonrpc_run()
| |--jsonrpc_send()
|--jsonrpc_recv()
|--process_command(conn, msg) // format output text
}
}
void
ovsdb_jsonrpc_server_run(struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_server *svr)
{
SHASH_FOR_EACH (node, &svr->remotes) {
struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_remote *remote = node->data;
pstream_accept(remote->listener, &stream);
jsonrpc_session_open_unreliably(jsonrpc_open(stream), remote->dscp);
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_create(remote, js, svr->read_only || remote->read_only);
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_run_all(remote);
|
|--LIST_FOR_EACH_SAFE (s, next, node, &remote->sessions)
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_run(s);
|--jsonrpc_sesion_recv()
msg->type:
case: ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_got_request(s, msg);
case: ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_got_notify(s, msg);
default: got unexpected msg();
}
}
handle RPC requests and make replies. The requests comes from many sources: some from the unixctl server, which converts CLI control messages into RPC requests; and from vswitchd.
static void
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_got_request(struct ovsdb_jsonrpc_session *s,
struct jsonrpc_msg *request)
{
switch(request->method) {
case "transact" if (!reply) reply = execute_transaction(s, db, request);
case "monitor" if (!reply) reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_monitor_create();
case "monitor_cond_change" reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_monitor_cond_change();
case "monitor_cancel" reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_monitor_cancel();
case "get_schema" if (!reply) reply = jsonrpc_create_reply();
case "list_dbs" reply = jsonrpc_create_reply();
case "lock" reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_lock();
case "steal" reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_lock();
case "unlock" reply = ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_unlock(s, request);
case "echo" reply = jsonrpc_create_reply();
}
if (reply) {
jsonrpc_msg_destroy(request);
ovsdb_jsonrpc_session_send(s, reply);
}
}
4.3 Execute OVSDB Session
void
ovsdb_trigger_run(struct ovsdb *db, long long int now)
{
LIST_FOR_EACH_SAFE (t, next, node, &db->triggers) {
if (run_triggers || now - t->created >= t->timeout_msec) {
ovsdb_trigger_try(t, now);
|--ovsdb_execute(t->db, t->session, t->request, ...)
|--ovsdb_txn_create()
|--parse and execute operations
|--ovsdb_txn_commit()
}
}
}