JuiceFS 元数据引擎三探:从实践中学习 TiKV 的 MVCC 和 GC(2024)

Fig. TiKV MVCC GC mechanisms.
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎初探:高层架构、引擎选型、读写工作流(2024)
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎再探:开箱解读 TiKV 中的 JuiceFS 元数据(2024)
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎三探:从实践中学习 TiKV 的 MVCC 和 GC(2024)
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎四探:元数据大小评估、限流与限速的设计思考(2024)
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎五探:元数据备份与恢复(2024)
水平及维护精力所限,文中不免存在错误或过时之处,请酌情参考。 传播知识,尊重劳动,年满十八周岁,转载请注明出处。
- 1 概念与实测
- 2 TiKV MVCC GC
- 3 GC 不及时导致的问题一例
- 4 问题讨论
- 参考资料
1 概念与实测
1.1 MVCC(多版本并发控制)
来自 wikipedia 的定义,
Multiversion concurrency control (MCC or MVCC), is a
non-lockingconcurrency control method commonly used by database management systems to provideconcurrent accessto the database and in programming languages to implementtransactionalmemory.
TiKV 支持 MVCC,当更新数据时,旧的数据不会被立即删掉,而是新老同时保留,以时间戳来区分版本。 官方有几篇很不错的博客 [1,3]。
下面进行一个简单测试来对 MVCC 有一个初步的直观认识。
1.1.2 TiKV MVCC 测试
参考上一篇,新创建一个新 volume,里面什么文件都没有,有 8 条记录,
$ tikv-ctl.sh scan --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' | grep "key:" | wc -l
8
然后进入这个 volume 的挂载目录,在里面创建一个文件,
$ cd <mount dir>
$ echo 1 > foo.txt
再次扫描这个 volume 对应的所有 keys,
$ tikv-ctl.sh scan --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' | grep "key:" | wc -l
16
可以看到变成 16 条记录,比之前多了 8 条。内容如下,依稀能看出大部分条目的用途 (行末的注释是本文加的),
key: zfoo-dev\375\377A\001\000\000\000\000\000\000\377\000Dfoo.tx\377t\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370 # foo.txt
key: zfoo-dev\375\377A\002\000\000\000\000\000\000\377\000C\000\000\000\000\000\000\375
key: zfoo-dev\375\377A\002\000\000\000\000\000\000\377\000I\000\000\000\000\000\000\371
key: zfoo-dev\375\377ClastCle\377anupFile\377s\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370 # lastCleanupFile
key: zfoo-dev\375\377ClastCle\377anupSess\377ions\000\000\000\000\373 # lastCleanupSessions
key: zfoo-dev\375\377CtotalIn\377odes\000\000\000\000\373 # totalInodes
key: zfoo-dev\375\377CusedSpa\377ce\000\000\000\000\000\000\371 # UsedSpace
key: zfoo-dev\375\377U\001\000\000\000\000\000\000\377\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370
接下来继续更新这个文件 1000 次(每次都是一个整数,由于文件内容极小,不会导致 TiKV 的 region split 等行为),
$ for n in {1..1000}; do echo $n > bar.txt; done
再次查看元数据条目数量:
$ tikv-ctl.sh scan --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' | grep key | wc -l
59
又多了 43 条。多的条目大致长这样:
key: zfoo-dev\375\377L\000\000\000\000f\356\221\377\231\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\3777\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370
key: zfoo-dev\375\377L\000\000\000\000f\356\221\377\233\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\377j\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370
key: zfoo-dev\375\377L\000\000\000\000f\356\221\377\234\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\377\235\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370
...
key: zfoo-dev\375\377L\000\000\000\000f\356\221\377\271\000\000\000\000\000\000\003\377\362\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\370
TiKV supports MVCC, which means that there can be multiple versions for the same row stored in RocksDB.
All versions of the same row share the same prefix(the row key) but havedifferent timestamps as a suffix.https://tikv.org/deep-dive/key-value-engine/rocksdb/
下面我们再看看执行以上文件更新操作期间,juicefs 客户端的日志。
1.1.2 JuiceFS client 日志
在执行以上 for 循环期间,JuiceFS client 的日志,
$ juicefs mount ...
...
<DEBUG>: PUT chunks/0/0/170_0_4 (req_id: "xx", err: <nil>, cost: 32.002516ms) [cached_store.go:669]
<DEBUG>: PUT chunks/0/0/171_0_4 (req_id: "xx", err: <nil>, cost: 32.002516ms) [cached_store.go:669]
<DEBUG>: PUT chunks/0/0/172_0_4 (req_id: "xx", err: <nil>, cost: 32.002516ms) [cached_store.go:669]
...
这个似乎对应的就是以上多出来的条目。
1.1.3 小结
本节的例子让我们看到,虽然 volume 里面从头到尾只有一个文件,
但随着我们不断覆盖这个文件内的值,元数据引擎 TiKV 内的条目数量就会持续增加。
多出来的这些东西,对应的就是这份数据的多个版本,也就是 MVCC 里面 multi-version 的表现。
显然,没有冲突的话,只保留最后一个版本就行了,其他版本都可以删掉 —— 这就是垃圾回收(GC)的作用。
1.2 GC(垃圾回收)
垃圾回收 (GC) 的功能是清理 MVCC 留下的旧版本。比如同一份数据保存了 1000 个版本,那原则上前面大部分版本都可以清掉了,只保留最新的一个或几个。
那如何判断哪些版本可以安全地清掉呢?TiKV 引入了一个时间戳概念:
safepoint。
GC is a process to clean up garbage versions (versions older than the configured lifetime) of each row.
https://tikv.org/deep-dive/key-value-engine/rocksdb/
1.3 Safepoint(可安全删除这个时间戳之前的版本)
In order to ensure the correctness of all read and write transactions, and make sure the GC mechanism works, TiKV/TiDB introduced the concept of safe-point. There is a guarantee that
all active transactions and future transactions’ timestamp is greater than or equal to the safe-point. It meansold versions whose commit-ts is less than the safe-point can be safely deletedby GC. [3]
2 TiKV MVCC GC
以上看到,TiKV 有 GC 功能,但由于其“历史出身”,也存在一些限制。
2.1 历史:从 TiDB 里面拆分出来,功能不完整
TiKV 是从 TiDB 里面拆出来的一个产品,并不是从一开始就作为独立产品设计和开发的。 这导致的一个问题是:MVCC GC 功能在使用上有点蹩脚:
- 默认情况下,靠底层 RocksDB 的 compaction 触发 GC,这周触发周期不确定且一般比较长;
- TiKV+PD 也内置了另一种 GC 方式,但并不会自己主动去做,而是将 GC 接口暴露出来,靠 TiDB 等在使用 TiKV 的更上层组件来触发(见下节的图);
tikv-ctl/pd-ctl等等命令行工具也都没有提供 GC 功能,这导致 TiKV 的运维很不方便,比如有问题想快速手动触发时用不了。
下面具体看看 TiKV 中的 GC 设计。
2.2 TiKV GC 设计和配置项

Fig. TiKV MVCC GC mechanisms.
2.2.1 设计:两种 GC 触发方式
- 被动 GC:TiKV 底层的 RocksDB compact 时进行垃圾回收。
- 通过 tikv-server 的 enable-compaction-filter 配置项控制;
- 默认启用;
- 触发 RocksDB compaction 时才能进行 GC。
tikv-ctl compact/compact-cluster可以手动触发这种 compact,进而 GC。
- 半主动 GC:内置了 GC worker,
- 定期获取 PD 里面的 gc safepoint,然后进行 GC;会占用一些 CPU/IO 资源;
- PD 不会主动更新这个 gc safepoint,一般是由在使用 TiKV 的更外围组件来更新的,例如 TiDB、JuiceFS 等等;
- 所以本文把这种方式称为“半主动”。
2.2.2 tikv-server 启动日志中的 GC 配置信息
tikv-server.log,
[INFO] [server.rs:274] ["using config"] [config="{..., "enable-compaction-filter":true, ...}"]
[INFO] [compaction_filter.rs:138] ["initialize GC context for compaction filter"]
[INFO] [gc_worker.rs:786] ["initialize compaction filter to perform GC when necessary"]
2.2.3 tikv-ctl compact/compact-cluster 触发被动 GC 例子
# compact-cluster 必须要指定 --pd 参数,因为针对是整个集群。指定 --host 会失败,但没有提示错在哪,TiKV 的命令行工具经常这样
$ tikv-ctl.sh compact-cluster --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop'
$ tikv-ctl.sh compact --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop'
store:"192.168.1.1:20160" compact db:Kv cf:default range:[[122, 122, 121, 110], [122, 122, 121, 111]) success!
$ tikv-ctl.sh compact --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' -c default # 很快
$ tikv-ctl.sh compact --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' -c lock # 很快
store:"192.168.1.1:20160" compact db:Kv cf:lock range:[[122, 122, 121, 110], [122, 122, 121, 111]) success!
$ tikv-ctl.sh compact --from 'zfoo' --to 'zfop' -c write # 非常慢
store:"192.168.1.1:20160" compact db:Kv cf:write range:[[122, 122, 121, 110], [122, 122, 121, 111]) success!
# 还可以指定本地 TiKV 数据路径直接 compact
# -d: specify the RocksDB that performs compaction. default: kv. Valid values: {kv, raft}
$ tikv-ctl --data-dir /path/to/tikv compact -d kv
2.2.4 小结
“半主动方式”需要外围组件去更新 PD 中的 gc safepoint 信息,这样下面的 TiKV 才会去执行 GC 操作。作为两个具体例子,我们接下来看看 TiDB 和 JuiceFS 在使用 TiKV 时,分别是怎么去更新这个信息的。
2.3 TiDB 中触发 TiKV GC 的方式
TiDB 有 GC 相关的配置和 worker,会按照配置去触发底层的 TiKV GC,

Fig. TiDB SQL layer overview. GC worker is outside of TiKV. Image Source: pingcap.com
更多信息可以参考 [3,4]。
2.4 JuiceFS 触发 TiKV GC 的方式
TiKV 作为元数据引擎时,JuiceFS 并没有使用 TiDB,而是直接使用的 TiKV(和 PD), 所以就需要 JuiceFS client 来触发这个 GC (因为不考虑 CSI 部署方式的话,JuiceFS 就一个客户端组件,也没有其他 long running 服务来做这个事情了)。
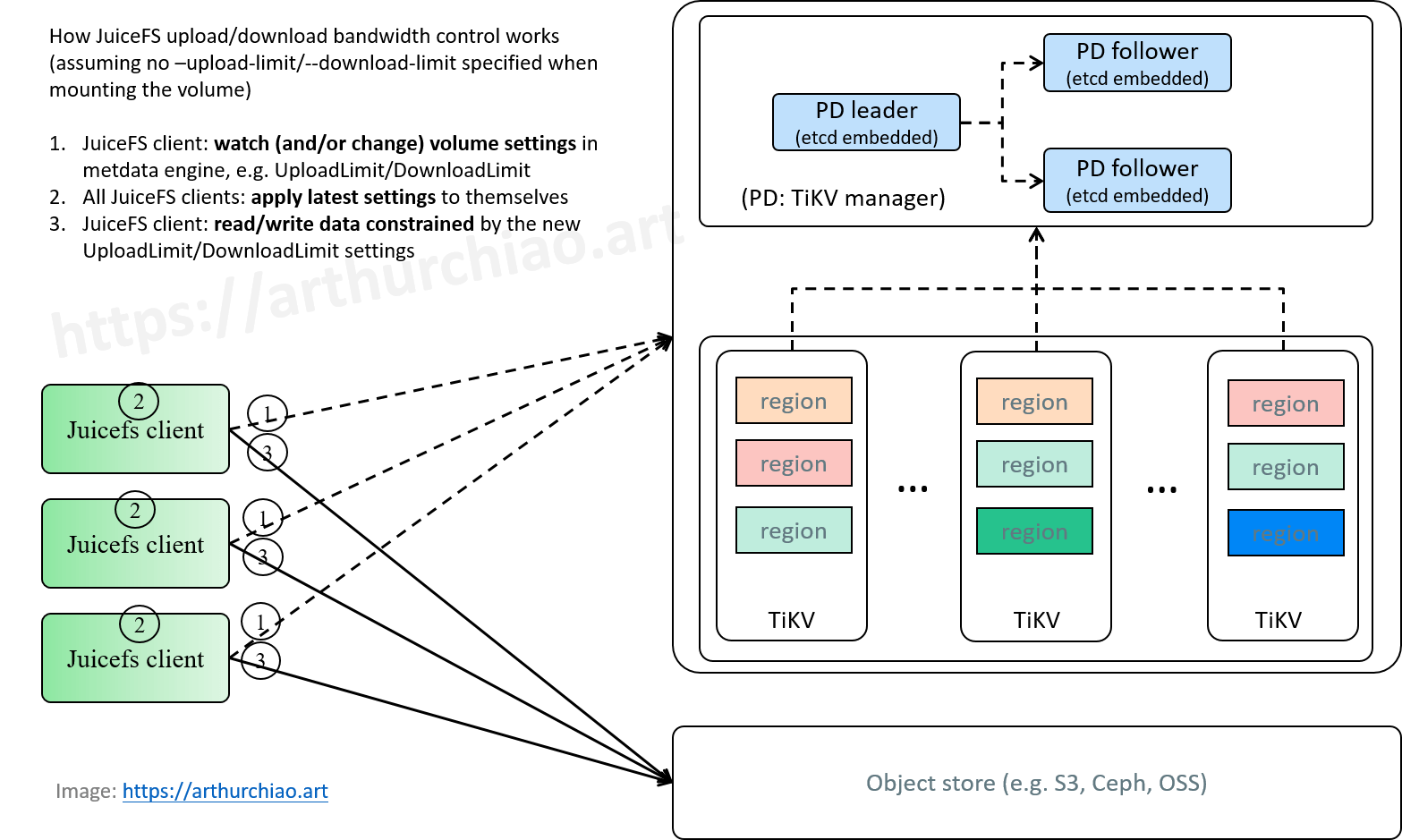
Fig. Typical JuiceFS cluster.
2.4.1 定期更新 gc safepoint 的代码
JuiceFS v1.0.4+ 客户端会周期性地设置 PD 中的 gc safepoint,默认是
now-3h,也就是可以删除 3 小时之前的旧版本数据,
// pkg/meta/tkv_tikv.go
func (c *tikvClient) gc() {
if c.gcInterval == 0 {
return
}
safePoint := c.client.GC(context.Background(), oracle.GoTimeToTS(time.Now().Add(-c.gcInterval)))
}
接下来的调用栈:
gc // github.com/juicedata/juicefs pkg/meta/tkv_tikv.go
|-c.client.GC // github.com/tikv/client-go tikv/gc.go
|-s.pdClient.UpdateGCSafePoint // github.com/tikv/pd client/client.go
|-ctx = grpcutil.BuildForwardContext(ctx, c.GetLeaderAddr())
|-c.getClient().UpdateGCSafePoint(ctx, req)
/
gRPC /
/----<--<----/
/
UpdateGCSafePoint // github.com/tikv/pd server/grpc_service.go
|-rc := s.GetRaftCluster()
|-oldSafePoint := s.storage.LoadGCSafePoint()
|-s.storage.SaveGCSafePoint(newSafePoint)
|-key := path.Join(gcPath, "safe_point") // gcPath = "gc"
|-value := strconv.FormatUint(safePoint, 16)
|-return s.Save(key, value)
2.4.2 配置:META URL \?gc-interval=1h
这个 gc-interval 可在 juicefs 挂载卷时加到 TiKV URL 中,
- 默认值:
3h - 最小值:
1h,设置的值小于这个值会打印一条 warning,然后强制设置为 1h。
juicefs client 挂载时显式设置 gc-interval,
$ juicefs mount tikv://localhost:2379\?gc-interval=1h ~/mnt/jfs
<INFO>: Meta address: tikv://localhost:2379?gc-interval=1h [interface.go:491]
<INFO>: TiKV gc interval is set to 1h0m0s [tkv_tikv.go:84]
...
2.4.3 juicefs gc 手动触发 TiKV GC
还可以通过 juicefs gc 子命令来主动触发 TiKV GC。这个例子中设置的时间太短,可以看到被强制改成了允许的最小值 1h,
$ juicefs gc tikv://<ip>:2379/foo-dev\?gc-interval=1m --delete
...
<WARNING>: TiKV gc-interval (1m0s) is too short, and is reset to 1h [tkv_tikv.go:133]
<INFO>: TiKV gc interval is set to 1h0m0s [tkv_tikv.go:138]
Cleaned pending slices: 0 0.0/s
Pending deleted files: 0 0.0/s
Pending deleted data: 0.0 b (0 Bytes) 0.0 b/s
Cleaned pending files: 0 0.0/s
Cleaned pending data: 0.0 b (0 Bytes) 0.0 b/s
Cleaned trash: 0 0.0/s
Cleaned detached nodes: 0 0.0/s
Listed slices: 2047 4930.4/s
Trash slices: 2026 55423.8/s
Trash data: 7.7 KiB (7883 Bytes) 211.8 KiB/s
Cleaned trash slices: 0 0.0/s
Cleaned trash data: 0.0 b (0 Bytes) 0.0 b/s
Scanned objects: 2047/2047 [===========================================] 18138.6/s used: 113.115519ms
Valid objects: 21 187.2/s
Valid data: 85.0 b (85 Bytes) 758.0 b/s
Compacted objects: 2026 18064.2/s
Compacted data: 7.7 KiB (7883 Bytes) 68.6 KiB/s
Leaked objects: 0 0.0/s
Leaked data: 0.0 b (0 Bytes) 0.0 b/s
Skipped objects: 0 0.0/s
Skipped data: 0.0 b (0 Bytes) 0.0 b/s
<INFO>: scanned 2047 objects, 21 valid, 2026 compacted (7883 bytes), 0 leaked (0 bytes), 0 delslices (0 bytes), 0 delfiles (0 bytes), 0 skipped (0 bytes) [gc.go:379]
2.5 外挂组件 github.com/tikv/migration/gc-worker
代码仓库,是个在 TiKV 之上的组件,
从 PD 获取 service safepoint 信息,然后计算 gc safepoint 并更新到 PD,从而触发 TiKV GC。
3 GC 不及时导致的问题一例
这里挑一个典型的问题讨论下。
3.1 问题现象
3.1.1 监控:TiKV db size 暴增,磁盘空间不断减小
如下面监控所示,

Fig. TiKV DB size soaring in a JuiceFS cluster, caused by TiKV GC lagging.
- TiKV DB size 暴增;
- TiKV region 分布出现显著变量,总数量也有一定程度上升;
- TiKV node 可用磁盘空间不断下降。
3.1.2 tikv-server 错误日志:failed to split region
查看 tikv-server 日志,看到一直在刷下面这样的 warning/error:
[WARN] [split_observer.rs:73] ["invalid key, skip"] [err="\"key 6E677... should be in (6E677..., 6E677...)\""] [index=0] [region_id=39179938]
[ERROR] [split_observer.rs:136] ["failed to handle split req"] [err="\"no valid key found for split.\""] [region_id=39179938]
[WARN] [peer.rs:2971] ["skip proposal"] [error_code=KV:Raftstore:Coprocessor] [err="Coprocessor(Other(\"[components/raftstore/src/coprocessor/split_observer.rs:141]: no valid key found for split.\"))"] [peer_id=39179939] [region_id=39179938]
也就是 region split 失败。
3.2 问题排查
- 根据日志报错,网上搜到一些帖子,初步了解问题背景(JuiceFS/TiKV 新人,接触没多久);
-
对报错日志进行分析,发现:
- 报错集中在几十个 region(
grep "failed to handle split req" tikv.log | awk '{print $NF}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -n -k1,1),相对总 region 数量很少; pd-ctl region-properties -r <region>看,发现 start/end key 都来自同一个 volume(命令行操作见下一篇);- 根据 volume 监控看,只有一个客户端
set请求非常高,每秒 400 次请求,而这个 volume 只有几个 GB,可以说非常小;
- 报错集中在几十个 region(
tikv-ctl mvcc -k <key>查看有问题的 key,发现超时了,报错说文件(元数据)太大;
结合以上三点,判断是某个或少数几个文件的 MVCC 版本太多,导致 TiKV split region 失败,进而不断累积垃圾数据。
3.3 问题根因
以上,猜测直接原因是这个用户 非正常使用 JuiceFS,疯狂更新文件,也就是我们 1.1 中例子的极端版。 这导致部分文件的历史版本极其多,TiKV 在 auto split region 时失败。网上也有一些类似的 case(大部分是 TiDB 用户)。
但本质上,还是因为 TiKV 的 GC 太滞后,
- 被动 GC(RocksDB compact 方式)的频率不可控,跟集群所有客户端的总 write/update/delete 行为有关;
-
JuiceFS 的主动 GC 频率太慢,跟不上某些文件的版本增长速度。
- JuiceFS 默认
now-3h,最小now-1h,也就是至少会保留一个小时内的所有版本(实际上我们是有个外部服务在定期更新 PD 的 gc safepoint,但也是设置的now-1h); - 根据监控看,异常的 juicefs client 每秒有
400+ set请求,一个小时就是 144w 次的更新(这些请求更新的文件很集中)。
- JuiceFS 默认
3.4 解决方式
- 写了个程序,允许以非常小的粒度去更新 PD 的 gc safepoint,例如
now-5m, 也就是最多保留最近 5 分钟内的版本,其他的都删掉;这一步下去就有效果了,先稳住了,DB 不再增长,开始缓慢下降; - 通知用户去处理那个看起来异常的客户端(我们没权限登录用户的机器,客户端不可控,这是另一个问题了)。
1+2,DB 开始稳步下降,最终完全恢复正常。
3.5 问题小结
对于 TiKV 这种 MVCC 的元数据引擎来说,JuiceFS 的一条元数据可能会保留多个版本,老版本什么时候删掉很大程度上依赖外部 GC 触发。 如果 GC 间隔太长 + 文件更新太频繁,单条元数据极端情况下就可以占几个 GB,这时候不仅 DB size 暴大,还会导致 TiKV split region 工作不正常。
4 问题讨论
前面看到,JuiceFS 支持配置 TiKV 的 GC 间隔,但从管理和运维层面,这里面也有几个问题可以探讨。
4.1 允许的最小 GC 间隔太大
目前最小是 now-1h,极端情况会导致第 3 节中的问题,TiKV DB size 暴增,集群被打爆。
4.2 GC 配置放在客户端,增加了用户的认知负担和学习成本
-
用户必需感知 TiKV gc 这个东西,增加认知成本和使用负担;
用户只是用 JuiceFS volume 读写文件,原则上没有必要去知道 JuiceFS 集群用什么元数据引擎, 甚至还必现了解这种元数据引擎的 GC 知识,后者都是 JuiceFS 集群管理员需要关心和解决的;
-
用户如果没有配置,就只完全依赖 RocksDB compaction 来 GC,更容易触发版本太多导致的问题。
4.3 管理员运维困境
用户一旦没有显式配置 gc-interval(使用很大的默认值),TiKV 可能就被打爆, 这种情况下用户不知道,管理员知道但可能没短平快的解决办法(不一定有权限管理用户的机器)。
4.4 小结
对集群管理员来说,更好的方式可能是,
- 有个(内部或外部)服务,可以按管理员的需求随时和/或定时去 GC;
- 用户侧完全不用感知这个事情;
- 有 Meta 操作的限流能力(可以隔离有问题的 volume 或 client),下一篇讨论。
参考资料
- MVCC in TiKV, pingcap.com, 2016
- JuiceFS 元数据引擎最佳实践:TiKV, juicefs.com
- Deep Dive into Distributed Transactions in TiKV and TiDB, medium.com, 2024
- MVCC garbage collection, TiDB doc, 2024

